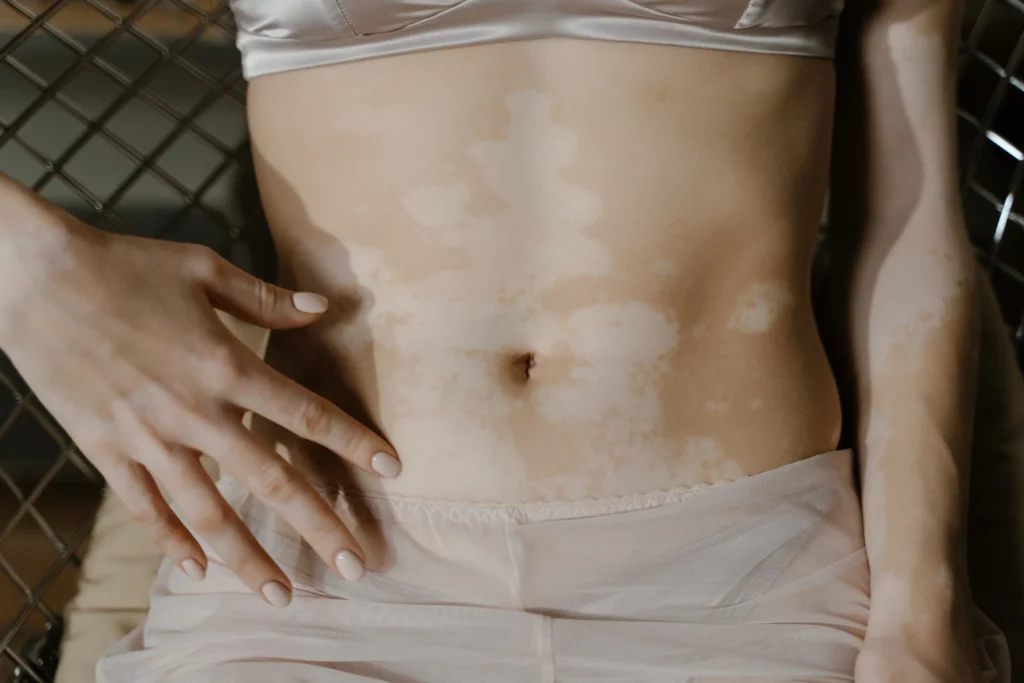
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by the loss of skin pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. It occurs when the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigment in the skin, die or stop functioning properly. Vitiligo can affect any part of the body, including the face, hands, feet, and genital area.
The cause of vitiligo is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the melanocytes. Vitiligo is not contagious or life-threatening, but it can cause psychological distress and affect a person’s quality of life. Treatment options for vitiligo include topical medications, phototherapy, and surgery.
Understanding Vitiligo: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Vitiligo is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic disease that causes white patches to develop on the skin due to the loss of melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin. Vitiligo affects people of all ages, races, and genders and can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Causes of Vitiligo
The exact cause of vitiligo is still unknown. However, researchers believe that it is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Other factors that may contribute to the development of vitiligo include genetic predisposition, sunburn, and exposure to certain chemicals.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
The primary symptom of vitiligo is the appearance of white patches on the skin. These patches may be small or large and may occur on any part of the body, including the face, hands, feet, and genital area. The patches may also appear on the mucous membranes, such as the inside of the mouth and nose. Other symptoms may include premature graying of the hair, loss of color in the retina, and an increased risk of sunburn.
Diagnosing Vitiligo
Diagnosing vitiligo is typically done through a physical examination by a dermatologist. The doctor may use a special lamp called a Wood’s lamp to examine the skin for signs of vitiligo. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out other autoimmune disorders. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.

Treatments for Vitiligo: Options and Effectiveness
While there is currently no cure for vitiligo, there are several treatment options available that can help to improve the appearance of the skin and reduce the psychological impact of the condition.
Topical Medications
Topical medications are a common treatment option for vitiligo, a skin condition characterized by the loss of skin pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and can help to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, which can be helpful in treating vitiligo.
Corticosteroids are a type of topical medication commonly used to treat vitiligo. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation in the skin, which can help to slow down or stop the progression of the disease. Corticosteroids can be applied as creams, ointments, or lotions and are available in varying strengths. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to side effects such as skin thinning and discoloration.
Calcineurin inhibitors are another type of topical medication that can be used to treat vitiligo. These medications work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation in the skin, similar to corticosteroids. However, calcineurin inhibitors are less likely to cause side effects such as skin thinning and discoloration, making them a preferred treatment option for some individuals. Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are two common calcineurin inhibitors used in the treatment of vitiligo.
In addition to corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, other topical medications may be used to treat vitiligo, including vitamin D analogs, retinoids, and topical psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy. Vitamin D analogs are used to help promote the growth and differentiation of melanocytes, while retinoids are used to help regulate cell growth and differentiation. Topical PUVA therapy involves the use of a psoralen medication applied to the skin, followed by exposure to UVA light.
While topical medications can be effective in treating vitiligo, they may take several months to show significant results, and there is a risk of side effects with prolonged use. It is important to work closely with a dermatologist to determine the appropriate course of treatment and to monitor for any potential side effects. In some cases, topical medications may be used in combination with other treatment options, such as phototherapy or surgery, to achieve the best possible outcome.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is a treatment option for vitiligo that involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. This type of therapy can stimulate the melanocytes to produce more pigment, which can help to improve the appearance of white patches on the skin.
There are two main types of phototherapy used to treat vitiligo: narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) and excimer laser. NB-UVB is the most common type of phototherapy and involves exposing the skin to a specific wavelength of UV light. This can be done in a doctor’s office or at home using a special light unit. Excimer laser therapy, on the other hand, involves delivering UV light directly to the affected areas of the skin using a handheld device.
Both types of phototherapy can be effective in treating vitiligo, but they do have some potential risks and side effects. These can include skin redness, itching, and burning, as well as an increased risk of skin cancer with prolonged exposure to UV light. Therefore, it is important to work closely with a dermatologist to determine the appropriate course of treatment and to monitor for any potential side effects.
Overall, phototherapy can be an effective treatment option for vitiligo, particularly for those with small to moderate patches of white skin. However, it is not suitable for everyone, and there are other treatment options available for those who may not benefit from phototherapy. It is important to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Surgery
Surgery is a treatment option for vitiligo that involves removing or transplanting melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin pigment, to the affected areas of the skin. It may be recommended for individuals with stable vitiligo, meaning the white patches on the skin are no longer spreading, and who have not responded well to other treatments such as topical medications or phototherapy.
There are several types of surgery used to treat vitiligo, including:
- Punch grafting: This involves removing small pieces of healthy skin from one area of the body and transplanting them to the affected areas of the skin. The transplanted skin contains melanocytes, which can help to restore skin pigmentation in the affected areas.
- Microskin grafting: This involves using a special device to remove a thin layer of skin from the donor site, which is then transplanted to the affected areas of the skin. This technique can produce a more natural-looking result than punch grafting.
- Tattooing: This involves tattooing the affected areas of the skin with pigments that match the individual’s skin tone. While this is not technically a surgical procedure, it can help to mask the white patches and improve the appearance of the skin.
- Melanocyte transplantation: This involves taking a sample of healthy skin from the individual and isolating melanocytes in a laboratory. The isolated melanocytes are then transplanted to the affected areas of the skin.
Surgery can be an effective treatment option for vitiligo, particularly for those with small to moderate patches of white skin. However, it is important to note that there are some potential risks and side effects associated with surgery, including infection, scarring, and changes in skin texture or color. Therefore, it is important to work closely with a dermatologist to determine the appropriate course of treatment and to monitor for any potential side effects.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. While there is no cure, there are several treatment options available that can help to improve the appearance of the skin and reduce the psychological impact of the condition. If you are experiencing symptoms of vitiligo, it is important to seek the advice of a dermatologist to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.